

Difference between Lab-Grown Diamonds and Natural Diamonds
The Origin of Natural Diamonds: Nature’s Billion-Year Art
Diamonds have fascinated us for centuries, but these mesmerizing marvels have a formation process that is rather a test of patience. They are formed when carbon atoms bond about 1 to 3 billion years, 100-200 kilometers under the Earth’s surface, under extreme temperature and high pressure over billions of years. Volcanic eruptions bring closer to the Earth’s surface, where humans discover and mine them through large-scale excavation.
Discover Elegance with Lab Created Diamond Pendants
Adorn yourself with pendants that radiate brilliance and responsibility. Our lab created diamond pendants combine timeless style with ethical beauty.
Shop PendantsFormation of Natural Diamonds
Step 1- Deep Earth Carbon
The carbon atoms are present about 145 to 200 km beneath the Earth’s surface, where temperatures rise over 1,100 Celsius and the pressure is over 5 gigapascals (GPa) - which is over 50,000 times greater than Earth’s atmospheric pressure (1 atm = 101.3 kPa) .
Step 2- Crystallization under Extreme Conditions
The carbon atoms bond in a specific way under these conditions to create a solid crystal, that we know as diamond.
Step 3- Erupt Your Way Out!
When powerful volcanic eruptions occur, they propel these crystals upward, in some cases quite near the Earth’s surface. The crystals are found in a type of rock known as Kimberlite.
Step 4- Extraction through Mining
When they get closer to the surface, the diamonds are mined from kimberlite pipes or riverbeds.
Step 5- Cutting, Faceting and Grading
Once mined, the diamonds are then cut, shaped and polished by expert gem cutters. They are then sent to labs which will grade them for the four Cs- Cut, Colour, Clarity and Carat.
The carbon atoms are present about 145 to 200 km beneath the Earth’s surface, where temperatures rise over 1,100 Celsius and the pressure is over 5 gigapascals (GPa) - which is over 50,000 times greater than Earth’s atmospheric pressure (1 atm = 101.3 kPa) .
Step 2- Crystallization under Extreme Conditions
The carbon atoms bond in a specific way under these conditions to create a solid crystal, that we know as diamond.
Step 3- Erupt Your Way Out!
When powerful volcanic eruptions occur, they propel these crystals upward, in some cases quite near the Earth’s surface. The crystals are found in a type of rock known as Kimberlite.
Step 4- Extraction through Mining
When they get closer to the surface, the diamonds are mined from kimberlite pipes or riverbeds.
Step 5- Cutting, Faceting and Grading
Once mined, the diamonds are then cut, shaped and polished by expert gem cutters. They are then sent to labs which will grade them for the four Cs- Cut, Colour, Clarity and Carat.
Shine Bright with Lab Grown Diamond Earrings
Elevate your everyday or special occasion look with sustainable sparkle. Explore our handcrafted lab grown diamond earrings today.
Explore EarringsWHAT ARE LAB-GROWN DIAMONDS?
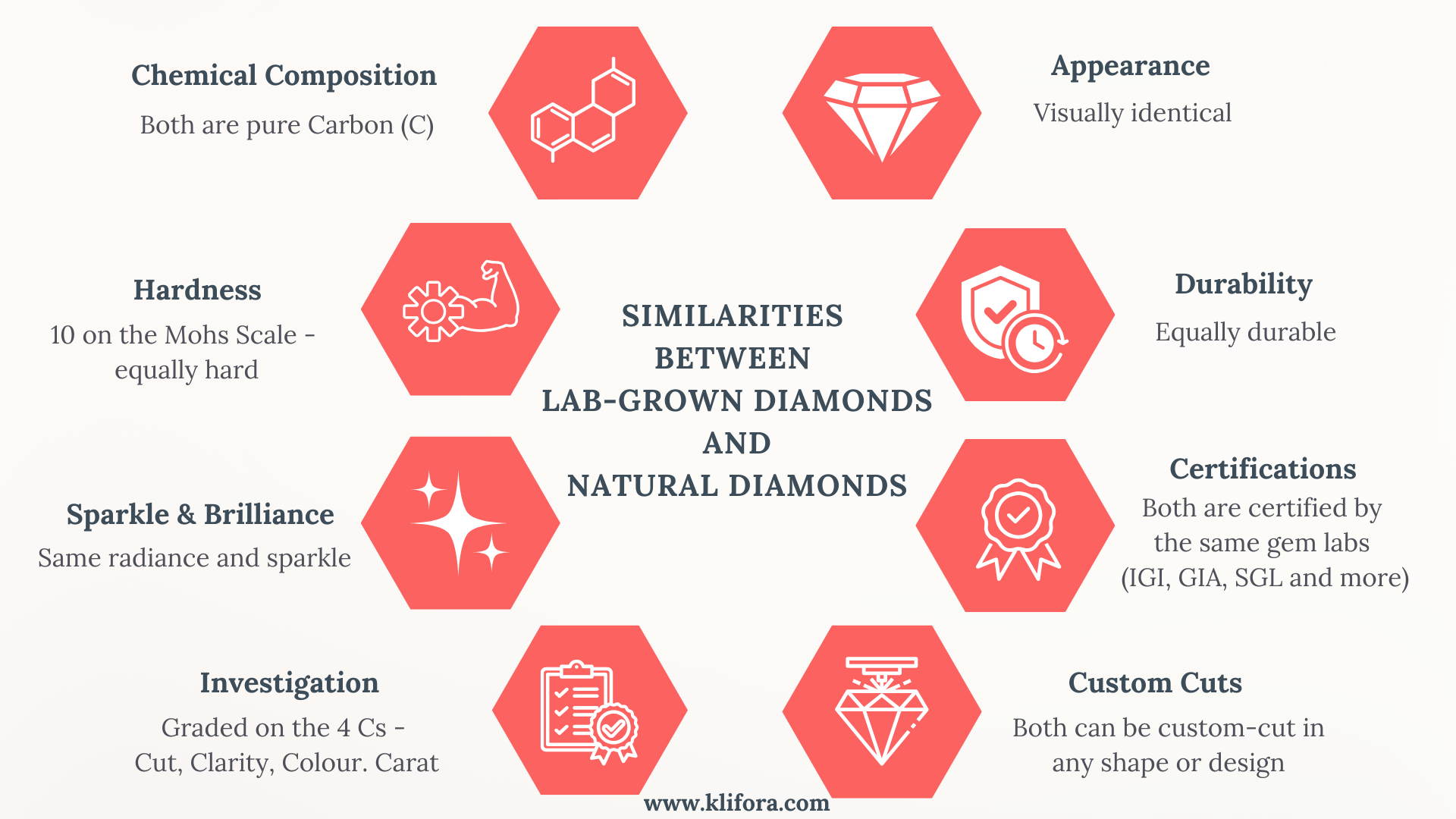
Lab-grown diamonds, which are also called artificial diamonds or man-made diamonds, are chemically, physically, and optically identical to natural diamonds. The only difference? Their origin.
Luxury & Ethics in Lab Created Diamond Necklaces
Make a statement with necklaces designed to sparkle with conscience. Our lab created diamond necklaces bring brilliance with purpose.
Shop NecklacesAre Lab-Made Diamonds Real?
Wondering whether lab-grown diamonds are real? YES! They are 100% real diamonds. These diamonds are grown in controlled lab environments, using cutting-edge technology that replicates the Earth’s natural diamond-forming process.
Celebrate Forever with Lab Grown Diamond Rings
From engagements to milestones, our lab grown diamond rings are crafted to symbolize love, responsibility, and elegance.
Browse Rings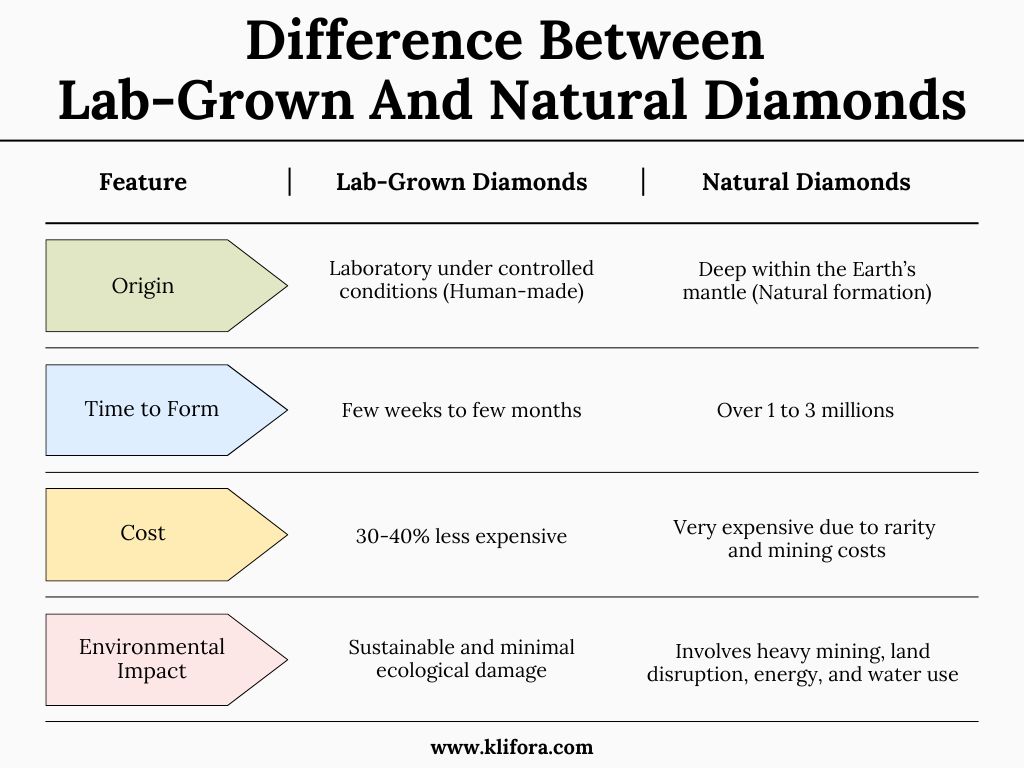

How Are Lab-Grown Diamonds Made?
Curious how diamonds are made in a lab? Let us take a brief look at the process.
- Diamond Seed: The central base is just a sliver of a natural or lab diamond (it is referred to as a seed).
- Growth Chamber: The seed is then put in a high tech chamber in one of two ways: 1)HPHT (High Pressure, High Temperature), 2) CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition)
- Carbon Crystallization: Carbon gas or graphite was added. Under the right conditions, the carbon atoms bond layn by layer forming a diamond crystal — the same exact way it happens in nature.
- Cutting & Polishing: The rough diamond is then cut and polished by a master gem cutter, similar to a mined diamond.
- Certification: Every lab-grown diamond comes with a certificate from top grading institutes such as IGI or GIA.
Shape the Future of Jewelry with Klifora
The future of franchising is ethical, scalable, and sustainable.
The future is lab grown.
The future is Klifora.
TYPES OF LAB-GROWN DIAMONDS
- HPHT Diamonds: They are produced under conditions of very high pressure and high temperatures by replicating the natural diamond-making conditions of the Earth.
- CVD Diamonds: They are made by gas deposition methods to grow diamonds of defined quality.
- Fancy Color Lab Diamonds: There were gorgeous hues—pink, blue, yellow—without the scarcity of rare minerals.

Why Are Lab-Grown Diamonds The Sustainable Choice?
Lab-grown diamonds are the future of luxury jewellery. Here's why:
Environment-Friendly: No more destructive mining, less use of water, and lower carbon emissions.
Conflict Free: 100% traceable and ethically sourced.
Affordable: You get the glitter for a fraction of the cost.
Diverse Options: From traditional whites to glowing fancy colors, the choices are limitless in the lab
So whenever you wonder… ‘lab-grown diamonds vs. real diamonds: what’s the difference?’ —the answer is obvious: they’re identical in splendor, but lab-grown wins in ethics, price and sustainability.
Explore Klifora’s low investment, high franchise business opportunities and be a part of the fast-growing lab-grown diamond revolution.
Environment-Friendly: No more destructive mining, less use of water, and lower carbon emissions.
Conflict Free: 100% traceable and ethically sourced.
Affordable: You get the glitter for a fraction of the cost.
Diverse Options: From traditional whites to glowing fancy colors, the choices are limitless in the lab
So whenever you wonder… ‘lab-grown diamonds vs. real diamonds: what’s the difference?’ —the answer is obvious: they’re identical in splendor, but lab-grown wins in ethics, price and sustainability.
Explore Klifora’s low investment, high franchise business opportunities and be a part of the fast-growing lab-grown diamond revolution.

 Contact Us
Contact Us